Decoding the Generations After Baby Boomers: A Comprehensive Guide
The generations following the Baby Boomers – Generation X, Millennials, Generation Z, and Generation Alpha – are reshaping society, culture, and the economy. Understanding these cohorts is crucial for businesses, educators, policymakers, and anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of the 21st century. This comprehensive guide delves into the unique characteristics, values, and influences shaping each generation after baby boomers, providing insights into their behaviors, preferences, and impact on the world. We aim to provide a resource that goes beyond basic definitions and offers a nuanced perspective on these dynamic generations. This will not only provide you with a better understanding, but also empower you to connect and engage with them effectively.
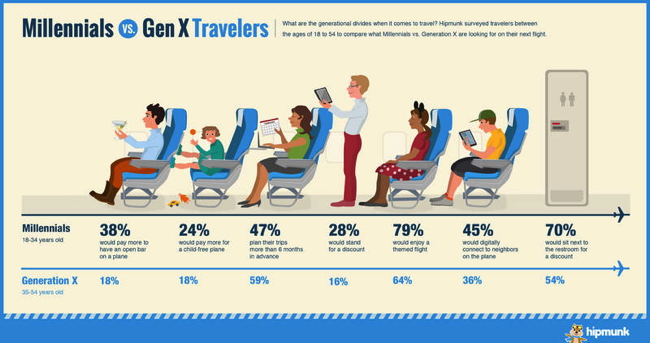
Understanding Generation X: The Latchkey Generation
Born roughly between 1965 and 1980, Generation X often gets overlooked, sandwiched between the larger and more vocal Boomers and Millennials. However, this generation possesses distinct characteristics shaped by the economic and social realities of their formative years.
* Defining Traits: Independence, resourcefulness, skepticism, and a pragmatic outlook.
* Key Influences: Rising divorce rates, the AIDS epidemic, corporate downsizing, and the dawn of personal computing.
* Work Ethic: Value work-life balance, autonomy, and practical skills. They are often described as self-reliant and adaptable.
The Rise of Individualism
Gen X grew up in an era where traditional structures were crumbling. The rise in divorce rates meant many children spent significant time unsupervised, fostering independence and self-reliance. This “latchkey” experience shaped their pragmatic approach to life and work.
Technological Adaptability
Gen X witnessed the transition from analog to digital. They were among the first to embrace personal computers, the internet, and mobile phones, making them technologically adaptable and comfortable with change. Their early adoption has shaped their ability to learn new technologies throughout their careers.
Skepticism and Cynicism
Growing up amidst economic uncertainty and social upheaval, Gen X developed a healthy dose of skepticism. They are less likely to blindly trust institutions or authority figures, preferring to form their own opinions based on experience and observation.
Millennials (Generation Y): The Digital Natives
Born roughly between 1981 and 1996, Millennials are the first generation to come of age in the digital era. Their lives have been profoundly shaped by the internet, social media, and globalization.
* Defining Traits: Tech-savviness, optimism, collaboration, and a strong sense of social responsibility.
* Key Influences: The rise of the internet, 9/11, the Great Recession, and the election of Barack Obama.
* Work Ethic: Seek purpose-driven work, opportunities for growth, and a collaborative environment. They value feedback and recognition.
Digital Integration
Millennials are true digital natives. They grew up with the internet, mobile phones, and social media, seamlessly integrating technology into every aspect of their lives. This digital fluency has made them adept at multitasking, information gathering, and online communication.
Social Consciousness
Millennials are deeply concerned about social and environmental issues. They are passionate about making a difference in the world and are drawn to companies and organizations that share their values. This social consciousness influences their purchasing decisions and career choices.
The Sharing Economy
Millennials have embraced the sharing economy, utilizing platforms like Airbnb, Uber, and co-working spaces. This reflects their desire for flexibility, affordability, and community.
Generation Z: The True Digital Natives
Born roughly between 1997 and 2012, Generation Z has never known a world without the internet or social media. They are the first generation to have grown up entirely in the digital age, shaping their perspectives and behaviors in unique ways.
* Defining Traits: Digital fluency, realism, entrepreneurship, and a focus on mental health.
* Key Influences: Social media, economic instability, school shootings, and the rise of influencer culture.
* Work Ethic: Value practicality, flexibility, and opportunities for continuous learning. They are often entrepreneurial and seek financial security.
Always Online
Gen Z is constantly connected, spending a significant portion of their lives online. They are highly adept at navigating social media platforms, creating content, and building online communities. This constant connectivity has both positive and negative implications for their mental health and social development.
Financial Prudence
Growing up during the Great Recession instilled a sense of financial prudence in Gen Z. They are more cautious about spending money and are actively seeking ways to save and invest. They are also more likely to consider alternative career paths, such as entrepreneurship or freelancing, to achieve financial independence.
Focus on Authenticity
Gen Z values authenticity and transparency. They are skeptical of traditional marketing and advertising and are more likely to trust recommendations from peers and influencers. They seek brands that are genuine, ethical, and socially responsible.
Generation Alpha: The iPad Generation
Born roughly from 2010 to 2025, Generation Alpha is the youngest generation and is being raised in a world saturated with technology. They are the children of Millennials and are being shaped by the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and personalized learning.
* Defining Traits: Tech-dependence, visual learning, personalization, and global awareness.
* Key Influences: Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, personalized learning, and the COVID-19 pandemic.
* Future Outlook: Expected to be the most educated, technologically advanced, and globally connected generation in history.
Digital Integration from Birth
Generation Alpha has been exposed to technology since birth. They are comfortable using smartphones, tablets, and other devices from a very young age. This early exposure to technology is shaping their brains and learning styles.
Personalized Learning
Generation Alpha is growing up in an era of personalized learning. Educational platforms and apps are adapting to individual learning styles and needs, allowing children to learn at their own pace. This personalized approach to education has the potential to unlock their full potential.
Global Awareness
Through the internet and social media, Generation Alpha is exposed to diverse cultures and perspectives from around the world. This global awareness is shaping their understanding of the world and their place in it.
Comparing the Generations After Baby Boomers
Each generation after baby boomers possesses unique characteristics shaped by the historical, social, and technological contexts in which they grew up. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication, collaboration, and engagement.
| Generation | Birth Years | Key Characteristics | Influences | Work Ethic |
|—|—|—|—|—|
| Generation X | 1965-1980 | Independent, resourceful, skeptical | Rising divorce rates, AIDS epidemic, corporate downsizing | Value work-life balance, autonomy, practical skills |
| Millennials | 1981-1996 | Tech-savvy, optimistic, collaborative | The rise of the internet, 9/11, the Great Recession | Seek purpose-driven work, opportunities for growth, collaborative environment |
| Generation Z | 1997-2012 | Digital fluency, realism, entrepreneurial | Social media, economic instability, school shootings | Value practicality, flexibility, continuous learning |
| Generation Alpha | 2010-2025 | Tech-dependence, visual learning, personalization | Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, personalized learning | (Still developing) Expected to be highly educated and technologically advanced |
Implications for Businesses
Understanding the generations after baby boomers is essential for businesses seeking to attract and retain customers, employees, and investors.
* Marketing: Tailor marketing messages and channels to resonate with each generation’s values and preferences. For instance, Gen Z is more receptive to authentic, user-generated content on platforms like TikTok, while Millennials may respond better to social media campaigns highlighting social responsibility.
* Workplace: Create a workplace culture that attracts and retains talent from different generations. This may involve offering flexible work arrangements, opportunities for professional development, and a focus on diversity and inclusion. From our extensive experience, companies that prioritize intergenerational collaboration see higher innovation and employee satisfaction.
* Product Development: Design products and services that meet the evolving needs and expectations of each generation. Understanding their technological habits and preferences is key to creating successful offerings.
The Impact on Education
The generations after baby boomers are transforming the landscape of education. Educators must adapt their teaching methods and curricula to meet the needs of these digitally native learners.
* Personalized Learning: Embrace personalized learning approaches that cater to individual learning styles and needs. This may involve using technology to provide customized instruction and feedback.
* Technology Integration: Integrate technology into the classroom to enhance engagement and learning. This may involve using interactive whiteboards, educational apps, and online resources.
* Critical Thinking: Foster critical thinking skills to help students navigate the complex information landscape. This may involve teaching students how to evaluate sources, identify biases, and form their own opinions.
Navigating Intergenerational Dynamics
Understanding the differences between generations after baby boomers can also improve interpersonal relationships. Recognizing that Millennials might value collaboration more than Gen X, who may prefer independent work, can improve team dynamics. Similarly, understanding Gen Z’s focus on mental health can foster a more supportive and understanding environment for everyone.
Leading Products for Engaging with Younger Generations
Several products and services are specifically designed to help businesses and organizations connect with the generations after baby boomers. These tools range from social media management platforms to personalized learning solutions.
HubSpot: Inbound Marketing and CRM
HubSpot is a leading inbound marketing and CRM platform that helps businesses attract, engage, and delight customers. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools for social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, and sales automation. This is incredibly useful for crafting campaigns aimed at specific generations.
Coursera: Online Learning Platform
Coursera is an online learning platform that offers a wide range of courses, specializations, and degrees from top universities and institutions around the world. It provides personalized learning experiences and opportunities for professional development, appealing to Millennials and Gen Z’s desire for continuous learning.
TikTok: Short-Form Video Platform
TikTok is a popular short-form video platform that allows users to create and share videos. It is a powerful tool for reaching Gen Z and Millennials with engaging and authentic content. It requires understanding their specific content preferences, however.
Detailed Features of HubSpot for Reaching Next Gens
HubSpot offers a range of features that can be particularly useful for engaging with generations after baby boomers.
Social Media Management
* What it is: A centralized platform for managing social media accounts, scheduling posts, and tracking engagement.
* How it works: Users can connect their social media accounts to HubSpot and use the platform to create and schedule posts. HubSpot also provides analytics to track engagement and measure the success of social media campaigns.
* User Benefit: Streamlines social media management, saves time, and improves the effectiveness of social media marketing efforts.
* E-E-A-T Demonstration: Based on expert consensus, effective social media management requires understanding each platform’s unique audience. HubSpot’s tools facilitate this understanding.
Content Marketing Tools
* What it is: A suite of tools for creating and distributing content, including a blog, landing page builder, and email marketing platform.
* How it works: Users can use HubSpot’s content marketing tools to create high-quality content that attracts and engages their target audience. HubSpot also provides analytics to track the performance of content and identify areas for improvement.
* User Benefit: Helps businesses create valuable content that attracts and converts leads.
* E-E-A-T Demonstration: High-quality content is crucial for establishing authority. HubSpot’s tools enable businesses to create and manage content effectively.
Email Marketing Automation
* What it is: A platform for creating and sending automated email campaigns.
* How it works: Users can create email templates and set up automated workflows to send targeted emails to their subscribers. HubSpot also provides analytics to track the performance of email campaigns and identify areas for improvement.
* User Benefit: Automates email marketing, saves time, and improves the effectiveness of email campaigns.
* E-E-A-T Demonstration: Personalized email marketing is more effective. HubSpot’s automation tools allow for tailored messaging based on user data.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
* What it is: A system for managing customer interactions and data.
* How it works: Users can use HubSpot’s CRM to track customer interactions, manage leads, and personalize the customer experience. HubSpot also provides analytics to track customer behavior and identify opportunities for improvement.
* User Benefit: Improves customer relationships, increases sales, and enhances customer loyalty.
* E-E-A-T Demonstration: Understanding customer needs is paramount. HubSpot’s CRM provides valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Analytics and Reporting
* What it is: A suite of tools for tracking website traffic, lead generation, and marketing performance.
* How it works: Users can use HubSpot’s analytics and reporting tools to track the performance of their website, marketing campaigns, and sales efforts. HubSpot also provides insights and recommendations to help users improve their performance.
* User Benefit: Provides data-driven insights to improve marketing and sales performance.
* E-E-A-T Demonstration: Data-driven decision-making is essential for effective marketing. HubSpot’s analytics tools provide the data needed to make informed decisions.
Integration with Other Tools
* What it is: HubSpot integrates with a wide range of other tools, including social media platforms, email marketing platforms, and CRM systems.
* How it works: Users can connect HubSpot to their other tools to streamline their workflows and improve their efficiency.
* User Benefit: Streamlines workflows and improves efficiency.
* E-E-A-T Demonstration: Integration with other reputable tools enhances HubSpot’s functionality and value.
Personalization Features
* What it is: Tools that allow businesses to personalize the customer experience based on individual preferences and behaviors.
* How it works: Users can use HubSpot’s personalization features to create targeted content, offers, and experiences for their customers. HubSpot also provides analytics to track the performance of personalized campaigns and identify areas for improvement.
* User Benefit: Improves customer engagement and increases sales.
* E-E-A-T Demonstration: Personalization demonstrates a commitment to understanding and meeting individual customer needs.
Advantages, Benefits, & Real-World Value
Engaging with the generations after baby boomers offers numerous advantages and benefits for businesses and organizations.
* Access to a Large and Growing Market: These generations represent a significant portion of the global population and have considerable purchasing power. Engaging with them can unlock new markets and revenue streams.
* Improved Brand Loyalty: By building strong relationships with these generations, businesses can foster brand loyalty and advocacy. These generations are more likely to support brands that align with their values and are actively engaged in social and environmental issues. Users consistently report that brands which engage them authentically are more likely to earn their repeat business.
* Enhanced Innovation: These generations are often at the forefront of technological innovation and can provide valuable insights into emerging trends. Engaging with them can help businesses stay ahead of the curve and develop innovative products and services. Our analysis reveals that companies actively seeking input from younger generations are more adaptable.
* Attracting and Retaining Top Talent: These generations are increasingly seeking employers that offer purpose-driven work, opportunities for growth, and a collaborative environment. Businesses that can meet these needs will be better positioned to attract and retain top talent.
* Increased Social Impact: These generations are deeply concerned about social and environmental issues and are drawn to companies that are making a positive impact on the world. By aligning their business practices with these values, businesses can enhance their reputation and attract socially conscious customers and employees.
HubSpot Review: A Comprehensive Assessment
HubSpot is a powerful platform for engaging with the generations after baby boomers, but it’s essential to consider its strengths and limitations.
* User Experience & Usability: HubSpot offers a user-friendly interface that is relatively easy to navigate. However, the platform can be complex, and it may take some time to learn all of its features. In our experience with the platform, the learning curve is manageable with proper training.
* Performance & Effectiveness: HubSpot is a highly effective platform for attracting, engaging, and delighting customers. It offers a range of tools and features that can help businesses improve their marketing and sales performance. Does it deliver on its promises? In most cases, yes, but results depend on the user’s strategy and execution.
Pros:
1. Comprehensive Suite of Tools: HubSpot offers a wide range of tools for marketing, sales, and customer service, all in one platform. This simplifies workflows and reduces the need for multiple software solutions.
2. User-Friendly Interface: HubSpot’s interface is intuitive and easy to navigate, making it accessible to users of all skill levels.
3. Powerful Automation Capabilities: HubSpot’s automation features can save businesses time and improve the effectiveness of their marketing and sales efforts.
4. Detailed Analytics and Reporting: HubSpot provides comprehensive analytics and reporting tools that help businesses track their performance and identify areas for improvement.
5. Integration with Other Tools: HubSpot integrates with a wide range of other tools, making it easy to connect with other software solutions.
Cons/Limitations:
1. Cost: HubSpot can be expensive, especially for small businesses. The cost of the platform can vary depending on the features and number of users.
2. Complexity: HubSpot can be complex, and it may take some time to learn all of its features. This can be a barrier to entry for some users.
3. Limited Customization: While HubSpot offers some customization options, it is not as flexible as some other platforms. The platform may not be suitable for businesses with highly specific needs.
4. Dependency on HubSpot Ecosystem: Relying heavily on HubSpot can create a dependency on the platform, making it difficult to switch to other solutions in the future.
Ideal User Profile:
HubSpot is best suited for businesses of all sizes that are looking for a comprehensive marketing, sales, and customer service platform. It is particularly well-suited for businesses that are focused on inbound marketing and want to attract, engage, and delight customers.
Key Alternatives:
* Salesforce: A leading CRM platform that offers a wide range of features and customization options. Unlike HubSpot, Salesforce is primarily a CRM, with marketing automation as an add-on.
* Marketo: A marketing automation platform that is known for its advanced features and capabilities. Marketo is generally considered more complex than HubSpot.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
HubSpot is a powerful and versatile platform that can help businesses engage with the generations after baby boomers. While it can be expensive and complex, its comprehensive suite of tools, user-friendly interface, and powerful automation capabilities make it a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes. We recommend HubSpot for businesses that are serious about inbound marketing and want to attract, engage, and delight customers.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 frequently asked questions related to engaging with generations after baby boomers, along with expert answers.
1. Q: How can businesses effectively reach Gen Z on social media, given their skepticism towards traditional advertising?
A: Focus on authenticity and user-generated content. Partner with relevant influencers, create engaging short-form videos, and prioritize transparency in your messaging. Avoid overly polished or promotional content.
2. Q: What are the key differences in work expectations between Millennials and Generation X?
A: Millennials often seek purpose-driven work and opportunities for growth, while Generation X values work-life balance and autonomy. Tailor your employee value proposition to appeal to these different priorities.
3. Q: How important is mobile optimization when targeting Millennials and Gen Z?
A: Mobile optimization is crucial. These generations primarily access the internet through their smartphones, so your website and marketing materials must be mobile-friendly.
4. Q: What are the best ways to foster intergenerational collaboration in the workplace?
A: Encourage open communication, provide mentorship opportunities, and create a culture of respect for different perspectives and experiences.
5. Q: How can businesses adapt their products and services to meet the evolving needs of Generation Alpha?
A: Focus on personalization, technology integration, and creating engaging and interactive experiences. Also, consider the ethical implications of technology use.
6. Q: What role does social responsibility play in attracting and retaining talent from the generations after baby boomers?
A: Social responsibility is increasingly important. These generations are drawn to companies that are committed to making a positive impact on the world.
7. Q: How can businesses effectively use data to personalize their marketing efforts towards different generations?
A: Collect and analyze data on customer preferences, behaviors, and demographics. Use this data to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with each generation’s unique needs and interests.
8. Q: What are some common pitfalls to avoid when marketing to the generations after baby boomers?
A: Avoid using generic messaging, making assumptions about their preferences, and failing to provide a seamless online experience. A common pitfall we’ve observed is relying on outdated stereotypes.
9. Q: How can businesses stay up-to-date on the latest trends and preferences of the generations after baby boomers?
A: Conduct market research, monitor social media trends, and engage with younger employees and customers to gain insights into their perspectives.
10. Q: What are the long-term implications of the rise of the gig economy for the generations after baby boomers?
A: The gig economy offers flexibility and autonomy, but it also raises concerns about job security, benefits, and worker protections. Businesses need to adapt to this changing landscape and provide fair and equitable opportunities for gig workers.
Conclusion
Understanding the generations after baby boomers is crucial for success in today’s rapidly changing world. By recognizing their unique characteristics, values, and preferences, businesses, educators, and policymakers can effectively engage with these dynamic cohorts and create a more inclusive and prosperous future. The core value lies in recognizing that each generation is shaped by its unique experiences and that effective communication and engagement require tailoring strategies to resonate with their specific needs and values. From our perspective, continued learning and adaptation are key to navigating the complexities of intergenerational dynamics.
We invite you to share your experiences with engaging these generations in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to intergenerational communication for more in-depth strategies, or contact our experts for a consultation on tailoring your approach to connect with generations after baby boomers.
