Afghanistan Language: Unveiling the Linguistic Tapestry of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, a land steeped in history and cultural diversity, boasts a rich linguistic landscape. Understanding the Afghanistan language is crucial to comprehending its complex society, politics, and cultural heritage. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the primary languages of Afghanistan, Dari and Pashto, exploring their intricacies, historical significance, and contemporary relevance. We aim to provide an unparalleled resource that not only informs but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the linguistic diversity of Afghanistan.
Dari and Pashto: The Official Languages of Afghanistan
Afghanistan officially recognizes two languages: Dari (Persian) and Pashto. While both are Indo-European languages, they belong to different branches and possess distinct characteristics. Dari, a dialect of Persian, serves as the lingua franca and is widely understood throughout the country. Pashto, on the other hand, is primarily spoken by the Pashtun ethnic group, predominantly in the eastern and southern regions.
Dari: The Lingua Franca of Afghanistan
Dari, often referred to as Afghan Persian, is a dialect of Persian that has evolved over centuries in Afghanistan. It shares a high degree of mutual intelligibility with Iranian Persian and Tajik Persian, but it possesses unique features in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
* **Historical Roots:** Dari’s roots can be traced back to the classical Persian language of the medieval era. It served as the language of the royal court and literary circles for centuries, contributing significantly to Persian literature and culture.
* **Geographical Distribution:** Dari is predominantly spoken in the northern, western, and central regions of Afghanistan, including major cities like Kabul, Herat, and Mazar-i-Sharif. It also serves as a common language for communication between different ethnic groups.
* **Modern Usage:** Dari is widely used in government, education, media, and commerce. It is the language of choice for official documents, news broadcasts, and literary works. Its widespread usage makes it an essential language for anyone seeking to engage with Afghan society.
Pashto: The Language of the Pashtuns
Pashto is the language of the Pashtun people, an ethnic group that constitutes a significant portion of Afghanistan’s population. It belongs to the Eastern Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family and possesses its own distinct grammatical structure and vocabulary.
* **Historical Significance:** Pashto has a rich literary tradition, with a history dating back several centuries. It has played a crucial role in preserving Pashtun culture and identity.
* **Geographical Distribution:** Pashto is primarily spoken in the eastern and southern regions of Afghanistan, as well as in parts of Pakistan. Major Pashto-speaking cities in Afghanistan include Kandahar, Jalalabad, and Khost.
* **Modern Usage:** Pashto is used in government, education, and media in Pashtun-dominated areas. It is also the language of Pashtun poetry, music, and folklore. Understanding Pashto is essential for engaging with the Pashtun community and understanding their cultural perspectives.
The Interplay Between Dari and Pashto
Dari and Pashto coexist in Afghanistan, with varying degrees of influence and interaction. While Dari serves as the lingua franca, Pashto holds significant cultural and political importance for the Pashtun population. The relationship between the two languages is complex and often influenced by political and social factors.
Language Policy and Education
The Afghan government officially recognizes both Dari and Pashto and promotes their usage in education and government institutions. However, the implementation of language policy has often been uneven, with Dari often receiving more prominence in practice.
* **Education System:** In most schools, instruction is provided in both Dari and Pashto, particularly in areas where both languages are widely spoken. However, the availability of Pashto-language resources and qualified teachers may vary depending on the region.
* **Government Institutions:** Government institutions are required to use both Dari and Pashto in official communications. However, in practice, Dari is often the dominant language, particularly in central government offices.
Language and Identity
Language plays a crucial role in shaping identity and fostering a sense of belonging. In Afghanistan, Dari and Pashto are closely associated with specific ethnic groups, contributing to the country’s diverse cultural landscape.
* **Dari Speakers:** Dari is often associated with the Tajik, Hazara, and other Persian-speaking communities in Afghanistan. It serves as a symbol of cultural heritage and intellectual tradition for these groups.
* **Pashto Speakers:** Pashto is a symbol of Pashtun identity and cultural pride. It represents the unique traditions, values, and social structures of the Pashtun people.
Minority Languages of Afghanistan
In addition to Dari and Pashto, Afghanistan is home to a number of minority languages spoken by various ethnic groups. These languages contribute to the country’s rich linguistic diversity and cultural heritage. Some of the most prominent minority languages include:
* **Uzbek:** Spoken primarily in the northern regions of Afghanistan, Uzbek is a Turkic language closely related to other Central Asian languages.
* **Turkmen:** Also spoken in the northern regions, Turkmen is another Turkic language with a significant presence in Afghanistan.
* **Balochi:** Spoken in the southwestern regions, Balochi is an Iranian language closely related to Persian and Pashto.
* **Hazargi:** A dialect of Persian spoken by the Hazara people in central Afghanistan. It has distinct features in pronunciation and vocabulary.
* **Nuristani Languages:** A group of Indo-Iranian languages spoken in the remote Nuristan region of eastern Afghanistan. These languages are considered to be among the most archaic of the Indo-Iranian language family.
Challenges and Opportunities for Language Preservation
Like many multilingual societies, Afghanistan faces challenges in preserving and promoting its diverse linguistic heritage. Factors such as globalization, urbanization, and political instability can threaten the vitality of minority languages and cultural traditions.
Challenges
* **Language Endangerment:** Some minority languages are facing the threat of endangerment due to factors such as language shift, limited resources, and lack of official recognition.
* **Unequal Access to Education:** Unequal access to education in minority languages can hinder the development of literacy and cultural preservation efforts.
* **Political Instability:** Political instability and conflict can disrupt language preservation efforts and lead to the displacement of linguistic communities.
Opportunities
* **Language Revitalization Programs:** Supporting language revitalization programs can help to preserve and promote endangered languages.
* **Multilingual Education:** Promoting multilingual education can ensure that all students have access to quality education in their native languages.
* **Cultural Preservation Initiatives:** Supporting cultural preservation initiatives can help to safeguard the linguistic and cultural heritage of Afghanistan.
The Influence of Afghanistan Language on Regional Culture
The languages of Afghanistan have significantly influenced the regional culture, art, and literature. Dari, with its rich literary tradition, has contributed to the broader Persian cultural sphere, while Pashto has shaped the unique cultural identity of the Pashtun people. The interplay of these languages has created a vibrant and diverse cultural landscape in Afghanistan.
* **Literature:** Dari literature has produced renowned poets, writers, and scholars who have made significant contributions to Persian literature. Pashto literature has preserved Pashtun folklore, traditions, and values.
* **Music:** Dari and Pashto music reflect the diverse cultural traditions of Afghanistan. Both languages have their own unique musical styles, instruments, and lyrical themes.
* **Art:** The languages of Afghanistan have inspired various forms of artistic expression, including calligraphy, painting, and sculpture. These art forms often incorporate linguistic elements and cultural symbols.
Afghanistan Language and Modern Technology
The digital age presents both challenges and opportunities for the languages of Afghanistan. While the internet and social media can facilitate the spread of information and communication, they can also pose threats to language diversity and cultural preservation.
Challenges
* **Digital Divide:** The digital divide can limit access to online resources and opportunities for speakers of minority languages.
* **Dominance of English:** The dominance of English on the internet can marginalize other languages and cultures.
* **Lack of Digital Resources:** The lack of digital resources in minority languages can hinder their usage and development in the digital age.
Opportunities
* **Online Language Learning:** Online language learning platforms can provide access to language education for speakers of Dari, Pashto, and other Afghan languages.
* **Digital Content Creation:** Creating digital content in minority languages can help to promote their usage and cultural preservation.
* **Social Media Engagement:** Using social media to engage with linguistic communities can foster a sense of belonging and cultural pride.
The Importance of Translation Services for Afghanistan Language
In today’s globalized world, translation services play a crucial role in facilitating communication and understanding between different cultures and languages. For Afghanistan, translation services are essential for bridging the linguistic gap between Dari, Pashto, and other languages.
* **Business and Commerce:** Translation services are essential for facilitating international trade and investment in Afghanistan. Accurate translations of business documents, contracts, and marketing materials can help to build trust and foster successful business relationships.
* **Government and Diplomacy:** Translation services are crucial for diplomatic relations and international cooperation. Accurate translations of official documents, treaties, and diplomatic correspondence can help to ensure effective communication and mutual understanding.
* **Education and Research:** Translation services are essential for accessing knowledge and information from around the world. Accurate translations of academic articles, research papers, and educational materials can help to promote learning and innovation in Afghanistan.
* **Healthcare:** Translation services are critical for providing healthcare services to diverse linguistic communities. Accurate translations of medical records, patient instructions, and healthcare information can help to ensure that all patients receive quality care.
Expert Insights on Dari and Pashto
Leading linguists and cultural experts emphasize the importance of understanding the nuances of Dari and Pashto to fully appreciate the richness of Afghan culture. According to Dr. Fatima Amiri, a renowned linguist specializing in Dari, “Dari is not just a language; it’s a window into the soul of Afghan society. Its poetic expressions and philosophical depth reflect the centuries of cultural exchange and intellectual development in the region.” Professor Rahman Gul, a leading expert in Pashto literature, adds, “Pashto embodies the spirit of the Pashtun people – their resilience, their honor, and their deep connection to their land. Understanding Pashto is key to understanding the Pashtun worldview.”
Learning Afghanistan Language: Resources and Opportunities
For those interested in learning Dari or Pashto, a variety of resources and opportunities are available. Online language learning platforms, language schools, and cultural centers offer courses in both languages. Additionally, immersion programs and cultural exchange programs can provide valuable opportunities for language learners to immerse themselves in the Afghan culture and language.
* **Online Resources:** Websites and apps like Duolingo, Memrise, and Rosetta Stone offer introductory courses in Dari and Pashto.
* **Language Schools:** Language schools in major cities offer structured courses in Dari and Pashto, taught by qualified instructors.
* **Cultural Centers:** Cultural centers often organize language classes, cultural events, and workshops related to Dari and Pashto.
* **Immersion Programs:** Immersion programs offer intensive language training and cultural experiences in Afghanistan or other Dari/Pashto-speaking regions.
Q&A: Your Questions About Afghanistan Language Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about the languages of Afghanistan:
1. **Is Dari the same as Farsi?** Dari is a dialect of Persian, also known as Farsi. It’s mutually intelligible with Iranian Persian but has some distinct vocabulary and pronunciation differences.
2. **Is Pashto related to Dari?** Yes, both are Indo-European languages, but they belong to different branches. Dari is part of the Western Iranian branch, while Pashto is part of the Eastern Iranian branch.
3. **Which language is more widely spoken in Afghanistan?** Dari is more widely spoken as a lingua franca, but Pashto is the primary language for a significant portion of the population, especially in the south and east.
4. **Are there any dialects of Pashto?** Yes, Pashto has several dialects, the two main ones being Northern Pashto and Southern Pashto. These dialects differ in pronunciation and some vocabulary.
5. **What is the writing system used for Dari and Pashto?** Both Dari and Pashto use a modified version of the Arabic script.
6. **Are there loanwords in Dari and Pashto?** Yes, both languages have loanwords from Arabic, English, and other languages due to historical and cultural interactions.
7. **How difficult is it to learn Dari or Pashto for English speakers?** The difficulty depends on individual learning styles and motivation. However, both languages have grammatical structures and pronunciations that can be challenging for English speakers.
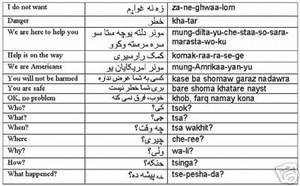
8. **What are some common phrases in Dari and Pashto?** In Dari: *Salam* (Hello), *Khoda hafez* (Goodbye), *Tashakor* (Thank you). In Pashto: *Pakheyr* (Hello), * خدا په آمان* (Khoda pa aman – Goodbye), *Manana* (Thank you).
9. **What role do Dari and Pashto play in Afghan national identity?** Both languages are central to Afghan national identity, representing different cultural and ethnic groups within the country.
10. **How can I support the preservation of minority languages in Afghanistan?** Supporting organizations that promote multilingual education, language documentation, and cultural preservation initiatives can help.
Conclusion: Embracing the Linguistic Diversity of Afghanistan
The Afghanistan language landscape, comprised primarily of Dari and Pashto, reflects the country’s rich cultural heritage and complex social dynamics. Understanding these languages is crucial for comprehending Afghan society, fostering cross-cultural understanding, and promoting effective communication. By embracing the linguistic diversity of Afghanistan, we can contribute to a more inclusive and harmonious future for the country.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the Afghanistan language and its significance. We encourage you to share your experiences with Dari and Pashto in the comments below. For further exploration, consider exploring our advanced guide to Persian literature or contacting our experts for a consultation on language learning resources.
