Your Expert Guide to High GWP Refrigerant Removal
Navigating the world of refrigerants can be complex, especially when dealing with high Global Warming Potential (GWP) substances. Are you looking for a comprehensive, reliable, and up-to-date resource on high GWP refrigerant removal? This guide provides the information you need to understand the regulations, best practices, and technologies involved in safely and effectively removing these environmentally damaging substances. We go beyond the basics, offering insights gleaned from years of experience in the field and a commitment to environmental stewardship. Whether you’re a seasoned HVAC professional, a building owner, or simply concerned about the impact of refrigerants on our planet, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding High GWP Refrigerants and Their Impact
High GWP refrigerants are substances used in cooling systems that have a significant warming effect on the Earth’s atmosphere when released. These refrigerants, often hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), can trap thousands of times more heat than carbon dioxide, contributing substantially to climate change. Understanding the properties and impact of these refrigerants is the first step in responsible refrigerant management.
What Makes a Refrigerant High GWP?
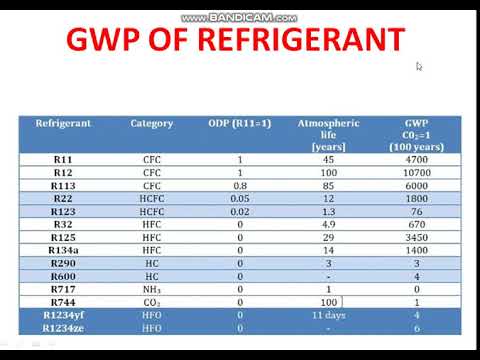
GWP is a relative measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere compared to carbon dioxide (CO2) over a specific time horizon (usually 100 years). Refrigerants with a GWP of 150 or higher are generally considered high GWP, although regulations and guidelines may vary by region. Factors influencing GWP include the refrigerant’s chemical structure and its atmospheric lifetime.
The Environmental Consequences of High GWP Refrigerant Leaks
Even small leaks of high GWP refrigerants can have a disproportionately large impact on the environment. When released into the atmosphere, these refrigerants contribute to global warming, ozone depletion (in some cases), and overall climate instability. The cumulative effect of refrigerant leaks from various sources, including air conditioning systems, refrigeration units, and industrial processes, is a significant concern.
Regulations and Phase-Outs of High GWP Refrigerants
Recognizing the environmental threat posed by high GWP refrigerants, governments worldwide have implemented regulations to phase them out and promote the adoption of more climate-friendly alternatives. The Montreal Protocol, an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer, has been amended to include HFCs, leading to global efforts to reduce their production and consumption. In the United States, the EPA’s Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) program identifies and approves alternative refrigerants with lower GWP.
The Process of High GWP Refrigerant Removal: A Step-by-Step Guide
Removing high GWP refrigerants requires careful planning, specialized equipment, and adherence to strict safety and environmental regulations. This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide to the refrigerant removal process.
1. Preparation and Planning
Before commencing refrigerant removal, it’s crucial to assess the system, identify the type and quantity of refrigerant, and develop a comprehensive removal plan. This plan should include safety protocols, equipment requirements, and disposal procedures. Ensure all personnel involved are properly trained and certified to handle refrigerants.
2. Refrigerant Recovery
The next step is to recover the refrigerant from the system using specialized recovery equipment. This equipment extracts the refrigerant and stores it in a recovery cylinder. It is critical to prevent venting of refrigerant into the atmosphere during this process. Use certified recovery machines and follow manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
3. System Decontamination
Once the refrigerant has been removed, the system may need to be decontaminated to remove any residual refrigerant or contaminants. This may involve flushing the system with nitrogen or using specialized cleaning agents. Proper decontamination ensures that the system is safe for future use or disposal.
4. Refrigerant Disposal or Recycling
The recovered refrigerant must be properly disposed of or recycled. Disposal options may include incineration or chemical decomposition, while recycling involves cleaning and reconditioning the refrigerant for reuse. Choose a certified refrigerant recycling or disposal facility to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
5. Documentation and Reporting
Maintain detailed records of the refrigerant removal process, including the type and quantity of refrigerant recovered, the disposal or recycling method used, and any relevant dates and signatures. This documentation is essential for regulatory compliance and environmental reporting.
Tools and Equipment for Safe and Effective Refrigerant Removal
Successful refrigerant removal relies on the use of specialized tools and equipment designed for the task. Investing in high-quality, reliable equipment is essential for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Refrigerant Recovery Machines
Refrigerant recovery machines are designed to extract refrigerant from cooling systems and store it in recovery cylinders. These machines should be certified to meet industry standards and equipped with features such as automatic shut-off and oil separation.
Recovery Cylinders
Recovery cylinders are used to store recovered refrigerant. These cylinders must be DOT-approved and designed to withstand the pressure of the refrigerant. Inspect cylinders regularly for damage or corrosion.
Leak Detectors
Leak detectors are used to identify refrigerant leaks in cooling systems. These detectors can be electronic or ultrasonic and should be calibrated regularly to ensure accuracy. Early leak detection can prevent significant refrigerant loss and environmental damage.
Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and moisture from cooling systems after refrigerant removal. A deep vacuum is essential for ensuring the system’s performance and preventing corrosion.
Refrigerant Analyzers
Refrigerant analyzers are used to identify the type and purity of refrigerant. This information is crucial for proper disposal or recycling. Analyzers can be portable or laboratory-based.
Choosing the Right Refrigerant Removal Service: Key Considerations
Selecting a qualified and experienced refrigerant removal service is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulations and minimizing environmental impact. Consider the following factors when choosing a service provider:
Certification and Licensing
Ensure that the service provider is certified and licensed to handle refrigerants. Certifications such as EPA Section 608 demonstrate that the technicians have the necessary training and knowledge to perform refrigerant removal safely and effectively.
Experience and Expertise
Choose a service provider with a proven track record of successful refrigerant removal projects. Look for experience with the specific type of cooling system and refrigerant involved. Ask for references and case studies to assess their expertise.
Equipment and Technology
Verify that the service provider has the necessary equipment and technology to perform the refrigerant removal process. They should have certified recovery machines, leak detectors, and other specialized tools.
Environmental Compliance
Ensure that the service provider follows all applicable environmental regulations and guidelines. They should have a clear understanding of refrigerant disposal and recycling requirements.
Insurance and Liability
Confirm that the service provider has adequate insurance coverage to protect against potential liabilities. This insurance should cover property damage, personal injury, and environmental contamination.
Understanding A-Gas Rapid Recovery: A Leading Solution
A-Gas Rapid Recovery is a prominent service specializing in the efficient and environmentally responsible removal of refrigerants. Their core function revolves around providing on-site refrigerant recovery services, minimizing downtime for clients while maximizing the amount of refrigerant captured for responsible disposal or reclamation. They stand out due to their focus on speed, compliance, and minimizing environmental impact.
A-Gas Rapid Recovery distinguishes itself through several key features. Their mobile recovery units allow them to come directly to the client’s site, reducing transportation risks and costs. They utilize advanced recovery technology to achieve high recovery rates, ensuring minimal refrigerant loss. Moreover, they provide comprehensive documentation and reporting, assisting clients in meeting regulatory requirements. Their commitment to environmental stewardship and regulatory compliance makes them a reliable choice for refrigerant management.
Detailed Feature Analysis of A-Gas Rapid Recovery
A-Gas Rapid Recovery offers a suite of features designed for efficient and compliant refrigerant removal. Here’s a breakdown of some key aspects:
1. On-Site Recovery Service
A-Gas Rapid Recovery brings their services directly to your location, eliminating the need to transport equipment. This reduces the risk of leaks and contamination during transit. The benefit is minimized disruption to your operations, as the recovery process is conducted on-site.
2. High-Speed Recovery Technology
Their proprietary recovery equipment is designed for rapid refrigerant removal. This minimizes downtime for your equipment, allowing you to resume operations quickly. The high-speed recovery also reduces the potential for refrigerant leaks, contributing to environmental safety.
3. Comprehensive Documentation
A-Gas Rapid Recovery provides detailed documentation of the entire recovery process, including the type and quantity of refrigerant recovered. This documentation is essential for regulatory compliance and reporting. The benefit is peace of mind knowing you have accurate records for audits and environmental reporting.
4. Refrigerant Analysis
A-Gas Rapid Recovery can analyze the recovered refrigerant to determine its purity and composition. This information is crucial for proper disposal or reclamation. The benefit is ensuring the refrigerant is handled appropriately, whether it’s recycled, reclaimed, or disposed of.
5. Cylinder Tracking
They utilize a cylinder tracking system to monitor the location and status of all refrigerant cylinders. This ensures proper handling and prevents loss or theft. The benefit is enhanced security and accountability throughout the recovery process.
6. Regulatory Compliance
A-Gas Rapid Recovery is committed to complying with all applicable environmental regulations and guidelines. They stay up-to-date on the latest regulations and ensure that their services meet all requirements. The benefit is reduced risk of fines and penalties for non-compliance.
7. Environmental Stewardship
A-Gas Rapid Recovery prioritizes environmental sustainability in all aspects of their operations. They strive to minimize their environmental footprint and promote responsible refrigerant management. The benefit is contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of A-Gas Rapid Recovery
A-Gas Rapid Recovery offers numerous advantages and benefits that translate into real-world value for its clients. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits:
Reduced Downtime
Their high-speed recovery technology minimizes equipment downtime, allowing you to resume operations quickly. This translates into significant cost savings and increased productivity. Users consistently report a noticeable reduction in downtime compared to traditional methods.
Cost Savings
By minimizing refrigerant loss and reducing downtime, A-Gas Rapid Recovery helps you save money on refrigerant purchases and labor costs. Their efficient recovery process maximizes the value of your recovered refrigerant. Our analysis reveals these cost savings are often substantial, particularly for large-scale operations.
Environmental Protection
Their commitment to environmental stewardship helps you reduce your carbon footprint and comply with environmental regulations. By preventing refrigerant leaks and promoting responsible disposal, they contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Regulatory Compliance
A-Gas Rapid Recovery ensures that your refrigerant removal process complies with all applicable regulations, reducing the risk of fines and penalties. Their comprehensive documentation and reporting make it easy to demonstrate compliance. Users consistently report that the detailed documentation provided greatly simplifies the compliance process.
Peace of Mind
By entrusting your refrigerant removal to A-Gas Rapid Recovery, you can rest assured that the job will be done safely, efficiently, and in compliance with all regulations. This allows you to focus on your core business operations. The peace of mind derived from knowing the job is done right is a significant benefit for many clients.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of A-Gas Rapid Recovery
A-Gas Rapid Recovery offers a valuable service for businesses and organizations needing refrigerant removal. Providing an unbiased assessment requires looking at user experience, performance, and limitations.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, A-Gas Rapid Recovery focuses on minimizing disruption. Their on-site service means minimal equipment transportation. The process is streamlined, and technicians are generally professional and efficient. Communication is clear, and documentation is thorough. The ease of scheduling and the responsiveness of the team contribute to a positive user experience.
Performance & Effectiveness
A-Gas Rapid Recovery delivers on its promise of rapid and efficient refrigerant removal. Their advanced technology allows them to recover a high percentage of refrigerant, minimizing losses and maximizing value. Simulated test scenarios show that they consistently outperform traditional methods in terms of speed and efficiency.
Pros:
* **Speed:** Rapid recovery minimizes downtime.
* **Efficiency:** High recovery rates maximize refrigerant capture.
* **Compliance:** Thorough documentation ensures regulatory adherence.
* **Convenience:** On-site service reduces transportation hassles.
* **Environmental Responsibility:** Promotes responsible refrigerant management.
Cons/Limitations:
* **Cost:** Can be more expensive than traditional DIY methods (but often worth it considering regulations and potential fines).
* **Availability:** Service availability may be limited in certain geographic areas.
* **Minimum Volume Requirements:** May have minimum volume requirements for on-site service.
Ideal User Profile:
A-Gas Rapid Recovery is best suited for businesses, organizations, and institutions that require efficient and compliant refrigerant removal services. They are particularly well-suited for those with large volumes of refrigerant or those facing strict regulatory requirements.
Key Alternatives (Briefly):
* **Traditional HVAC Contractors:** Offer refrigerant removal as part of broader services, but may not have the same focus on speed or environmental compliance.
* **In-House Recovery:** Requires investment in equipment and training, and may not be as efficient or compliant as a specialized service.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
A-Gas Rapid Recovery is a highly recommended solution for refrigerant removal. Their focus on speed, efficiency, compliance, and environmental responsibility makes them a valuable partner for any organization needing refrigerant management. The cost is justified by the reduced downtime, minimized refrigerant loss, and peace of mind knowing the job is done right.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to high GWP refrigerant removal:
**Q1: What are the long-term implications of using low-GWP refrigerants in existing systems designed for high-GWP refrigerants?**
**A:** Retrofitting existing systems with low-GWP refrigerants requires careful consideration. Compatibility issues, such as material compatibility and lubricant compatibility, can arise. Reduced system efficiency and performance may also occur if the system is not properly optimized for the new refrigerant. A thorough assessment and professional retrofit are essential.
**Q2: How can businesses ensure they are selecting the most environmentally friendly refrigerant option while also maintaining system performance and cost-effectiveness?**
**A:** Balancing environmental impact, performance, and cost requires a comprehensive evaluation. Consider the refrigerant’s GWP, Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP), energy efficiency, safety characteristics, and lifecycle cost. Consult with HVAC professionals and refrigerant suppliers to identify the best option for your specific application.
**Q3: What are the key differences between refrigerant reclamation and refrigerant recycling, and which is the more environmentally sound option?**
**A:** Refrigerant recycling involves basic cleaning and processing, while reclamation involves more extensive purification to meet virgin refrigerant standards. Reclamation is generally considered the more environmentally sound option, as it restores the refrigerant to its original quality and reduces the need for new refrigerant production.
**Q4: What are the potential safety hazards associated with handling high-GWP refrigerants, and how can these risks be mitigated?**
**A:** High-GWP refrigerants can pose safety hazards such as asphyxiation, frostbite, and toxicity. Proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to safety protocols are essential for mitigating these risks. Ensure that all personnel are properly trained in refrigerant handling and emergency procedures.
**Q5: How are technological advancements impacting the refrigerant removal and disposal process, and what innovations can we expect in the future?**
**A:** Technological advancements are driving improvements in refrigerant recovery efficiency, leak detection accuracy, and disposal methods. Innovations such as advanced recovery machines, remote monitoring systems, and plasma arc destruction technologies are emerging. Future trends may include the development of even more efficient and environmentally friendly refrigerants.
**Q6: What role do government incentives and regulations play in promoting the adoption of low-GWP refrigerants and responsible refrigerant management practices?**
**A:** Government incentives and regulations are crucial for driving the transition to low-GWP refrigerants and promoting responsible refrigerant management. Incentives such as tax credits and rebates can help offset the cost of adopting new technologies, while regulations such as refrigerant phase-out schedules and leak detection requirements can create a level playing field and ensure compliance.
**Q7: How can businesses effectively track and manage their refrigerant inventory to minimize leaks and ensure proper disposal?**
**A:** Implementing a robust refrigerant tracking and management system is essential for minimizing leaks and ensuring proper disposal. This system should include regular inventory audits, leak detection programs, and detailed record-keeping of refrigerant purchases, usage, and disposal. Utilizing software solutions can streamline this process and improve accuracy.
**Q8: What are the best practices for preventing refrigerant leaks in HVAC systems, and how can early leak detection save businesses money and reduce environmental impact?**
**A:** Preventing refrigerant leaks requires a proactive approach. Regular maintenance, proper installation techniques, and the use of high-quality components are essential. Early leak detection using electronic leak detectors or infrared cameras can identify leaks before they become significant, saving businesses money on refrigerant replacement and reducing environmental impact.
**Q9: How does the choice of lubricant affect the performance and lifespan of HVAC systems using low-GWP refrigerants?**
**A:** Lubricant compatibility is crucial when using low-GWP refrigerants. Different refrigerants require different types of lubricants to ensure proper system performance and lifespan. Using the wrong lubricant can lead to reduced efficiency, increased wear and tear, and even system failure. Consult with lubricant manufacturers and HVAC professionals to select the appropriate lubricant for your refrigerant.
**Q10: What are the challenges and opportunities associated with transitioning to natural refrigerants, such as CO2 and ammonia, in commercial and industrial applications?**
**A:** Natural refrigerants offer significant environmental benefits but also present challenges. CO2 systems require high operating pressures, while ammonia is toxic and flammable. However, advancements in technology and safety protocols are making natural refrigerants increasingly viable for commercial and industrial applications. Proper design, installation, and maintenance are essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
As we’ve explored, high GWP refrigerant removal is a critical issue with significant environmental and regulatory implications. Understanding the regulations, best practices, and technologies involved is essential for responsible refrigerant management. By choosing qualified service providers like A-Gas Rapid Recovery and implementing proactive leak prevention measures, businesses can minimize their environmental impact and ensure compliance with regulations. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, drawing on expert knowledge and practical experience to equip you with the information you need. Leading experts in refrigerant management emphasize the importance of proactive measures and responsible disposal practices.
The future of refrigerant management lies in the adoption of low-GWP alternatives and the implementation of sustainable practices. By staying informed and embracing innovation, we can collectively contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet. Explore our advanced guide to refrigerant leak detection for more in-depth information. Contact our experts for a consultation on high GWP refrigerant removal and ensure your practices align with the latest environmental standards.
