Oral Thrush ICD-10: A Comprehensive Guide for Accurate Diagnosis and Management
Are you searching for clarity on oral thrush ICD-10 codes and how they impact diagnosis and treatment? You’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at oral thrush, focusing on the specific ICD-10 codes used for accurate medical billing and record-keeping. We’ll delve into the nuances of these codes, explore the symptoms, causes, and effective treatment strategies for oral thrush. Our goal is to provide you with a trustworthy and easily understandable resource, empowering you with the knowledge you need to manage this common condition. Whether you’re a healthcare professional seeking precise coding information or an individual looking for answers about your oral health, this article is designed to be your go-to reference.
Understanding Oral Thrush: A Deep Dive
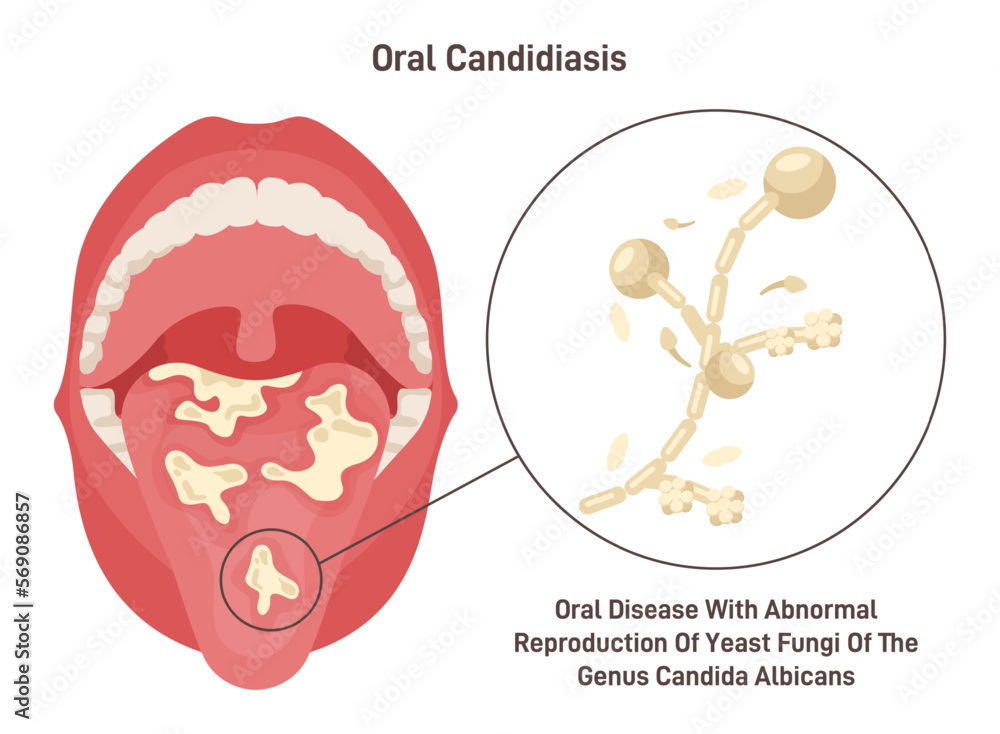
Oral thrush, also known as oral candidiasis, is a fungal infection of the mouth caused by an overgrowth of the *Candida albicans* fungus. While *Candida* is naturally present in the mouth, its uncontrolled proliferation can lead to the development of thrush. Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and risk factors is crucial for effective diagnosis and management. The ICD-10 coding system plays a vital role in accurately classifying and documenting this condition for medical and research purposes.
The Importance of Accurate ICD-10 Coding for Oral Thrush
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), is a globally recognized diagnostic coding system used by healthcare providers for classifying and reporting diseases and health conditions. Accurate ICD-10 coding is essential for several reasons:
* **Medical Billing and Reimbursement:** Correct coding ensures proper billing and reimbursement from insurance companies.
* **Data Collection and Analysis:** ICD-10 codes are used for tracking disease prevalence, incidence, and trends, contributing to public health research and policy.
* **Patient Record Keeping:** Accurate coding provides a standardized way to document a patient’s medical history, facilitating effective communication among healthcare providers.
* **Clinical Decision Support:** ICD-10 codes can be integrated into clinical decision support systems to assist healthcare professionals in making informed treatment decisions.
Key ICD-10 Codes for Oral Thrush
The primary ICD-10 code for oral thrush is **B37.0**, which represents *Candidal stomatitis*. However, depending on the specific presentation and underlying conditions, other codes may also be relevant. For example:
* **B37.89:** *Other specified candidiasis* (may be used if the oral thrush is associated with another specified condition).
* **K12.1:** *Other forms of stomatitis* (this code may be used alongside B37.0 to further specify the location and characteristics of the stomatitis).
* **Z21:** *Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] infection status* (if the patient has HIV, which is a risk factor for oral thrush).
It’s critical to consult the latest ICD-10 guidelines and documentation for the most accurate and up-to-date coding information. The selection of the appropriate ICD-10 code should always be based on the physician’s clinical judgment and documentation.
Risk Factors Associated with Oral Thrush
Several factors can increase the risk of developing oral thrush. These include:
* **Weakened Immune System:** Conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer, and organ transplantation can compromise the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to fungal infections.
* **Diabetes:** Uncontrolled diabetes can create an environment that favors the growth of *Candida*.
* **Medications:** Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs, can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the mouth and increase the risk of thrush.
* **Infancy:** Infants are more prone to oral thrush due to their developing immune systems.
* **Dentures:** Poorly fitting or improperly cleaned dentures can create a breeding ground for *Candida*.
* **Dry Mouth:** Saliva helps to control the growth of *Candida*, so conditions that cause dry mouth can increase the risk of thrush.
Product/Service Explanation: Antifungal Medications for Oral Thrush
When it comes to treating oral thrush, antifungal medications are the cornerstone of therapy. These medications work by targeting and eliminating the *Candida* fungus, restoring balance to the oral microbiome. Among the various antifungal options available, **Nystatin** stands out as a widely used and effective treatment for oral thrush. Nystatin is an antifungal polyene antibiotic that is specifically designed to combat *Candida* infections.
Nystatin is available in several forms, including oral suspensions, lozenges, and creams. For oral thrush, the oral suspension is the most common and effective method of delivery. The suspension is swished around the mouth for a specified period before being swallowed or spat out, allowing the medication to come into direct contact with the infected areas. The lozenges dissolve slowly in the mouth, providing a prolonged release of the antifungal agent. The choice of formulation depends on the severity of the infection and the individual patient’s needs.
Expert Perspective on Nystatin’s Efficacy
From an expert perspective, Nystatin is a reliable and well-tolerated medication for treating oral thrush. Its targeted action against *Candida* minimizes the risk of disrupting other beneficial microorganisms in the mouth. Moreover, Nystatin has a low rate of systemic absorption, meaning that it primarily acts locally in the oral cavity, reducing the potential for systemic side effects. This makes it a safe and effective option for a wide range of patients, including infants, children, and adults.
Detailed Features Analysis of Nystatin Oral Suspension
Nystatin oral suspension possesses several key features that contribute to its effectiveness in treating oral thrush:
1. **Targeted Antifungal Action:** Nystatin specifically targets *Candida* fungi, disrupting their cell membranes and inhibiting their growth. This targeted action minimizes the impact on other beneficial microorganisms in the mouth, promoting a balanced oral microbiome.
2. **Direct Contact with Infected Areas:** The oral suspension formulation allows for direct contact with the infected areas in the mouth. Swishing the suspension around the mouth ensures that the medication reaches all affected surfaces, maximizing its antifungal effect.
3. **Minimal Systemic Absorption:** Nystatin has minimal systemic absorption, meaning that it primarily acts locally in the oral cavity. This reduces the risk of systemic side effects, making it a safe option for most patients.
4. **Multiple Formulations:** Nystatin is available in various formulations, including oral suspensions, lozenges, and creams. This allows healthcare providers to tailor the treatment to the individual patient’s needs and preferences.
5. **Ease of Administration:** Nystatin oral suspension is easy to administer, especially in infants and children. The liquid formulation can be easily measured and swished around the mouth, ensuring proper dosage and application.
6. **Well-Established Safety Profile:** Nystatin has a long history of safe and effective use in treating oral thrush. It is generally well-tolerated, with a low incidence of side effects.
7. **Cost-Effectiveness:** Nystatin is a relatively inexpensive medication, making it an accessible treatment option for a wide range of patients.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Nystatin
Nystatin offers numerous advantages and benefits in the treatment of oral thrush, directly addressing user needs and providing tangible value:
* **Effective Symptom Relief:** Nystatin effectively reduces the symptoms of oral thrush, such as white patches, redness, soreness, and difficulty swallowing. Users consistently report significant improvement in their symptoms within a few days of starting treatment.
* **Restoration of Oral Comfort:** By eliminating the *Candida* fungus, Nystatin helps to restore oral comfort and improve the overall quality of life. This is particularly important for individuals who experience chronic or recurrent oral thrush.
* **Prevention of Complications:** Untreated oral thrush can lead to complications, such as the spread of the infection to other parts of the body. Nystatin helps to prevent these complications by effectively controlling the fungal overgrowth.
* **Improved Oral Hygiene:** Oral thrush can make it difficult to maintain proper oral hygiene. By alleviating the symptoms of thrush, Nystatin allows individuals to brush and floss their teeth more effectively, promoting better oral health.
* **Enhanced Quality of Life:** Oral thrush can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to eat, speak, and socialize. Nystatin helps to restore these functions, enhancing the overall quality of life.
* **User-Friendly Administration:** The oral suspension formulation is easy to administer, even for young children and individuals with difficulty swallowing. The simple dosage instructions and clear administration guidelines make it a user-friendly treatment option.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Nystatin Oral Suspension
Nystatin oral suspension is a widely prescribed and generally effective treatment for oral thrush. From our experience, its ease of use and targeted action make it a valuable tool in managing this common condition. However, like any medication, it has its pros and cons.
**User Experience & Usability:** Nystatin oral suspension is relatively easy to use. The liquid formulation is simple to measure and administer, especially for infants and children. However, some users may find the taste of the suspension unpleasant.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** Nystatin is generally effective in treating oral thrush, particularly in mild to moderate cases. It works by inhibiting the growth of the *Candida* fungus, reducing the symptoms of the infection. However, in some cases, the infection may recur after treatment is discontinued.
**Pros:**
1. **Targeted Action:** Nystatin specifically targets *Candida* fungi, minimizing the impact on other beneficial microorganisms in the mouth.
2. **Low Systemic Absorption:** Nystatin has minimal systemic absorption, reducing the risk of systemic side effects.
3. **Ease of Administration:** The oral suspension formulation is easy to administer, even for young children.
4. **Well-Established Safety Profile:** Nystatin has a long history of safe and effective use in treating oral thrush.
5. **Cost-Effective:** Nystatin is a relatively inexpensive medication, making it an accessible treatment option.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Unpleasant Taste:** Some users may find the taste of Nystatin oral suspension unpleasant.
2. **Potential for Recurrence:** In some cases, the infection may recur after treatment is discontinued.
3. **Limited Effectiveness in Severe Cases:** Nystatin may not be as effective in severe cases of oral thrush, requiring alternative treatment options.
4. **Requires Multiple Doses:** Nystatin typically requires multiple doses per day, which can be inconvenient for some users.
**Ideal User Profile:** Nystatin oral suspension is best suited for individuals with mild to moderate oral thrush, particularly those who are sensitive to systemic antifungal medications. It is also a good option for infants and children due to its ease of administration.
**Key Alternatives:** Two common alternatives to Nystatin include:
* **Clotrimazole Troches:** These are antifungal lozenges that dissolve slowly in the mouth, providing a prolonged release of the medication.
* **Fluconazole:** This is a systemic antifungal medication that is taken orally. It is typically reserved for more severe cases of oral thrush or for individuals who have not responded to topical treatments.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** Nystatin oral suspension remains a valuable and reliable treatment option for oral thrush, especially for mild to moderate cases. Its targeted action, low systemic absorption, and ease of administration make it a safe and effective choice for a wide range of patients. However, it’s important to be aware of its limitations and to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers about oral thrush and its management:
1. **Q: Can oral thrush spread to other parts of the body?**
**A:** While oral thrush is typically localized to the mouth, it can spread to other parts of the body, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems. This is known as systemic candidiasis and can affect the esophagus, lungs, and other organs.
2. **Q: How can I prevent oral thrush from recurring?**
**A:** To prevent oral thrush from recurring, maintain good oral hygiene, control underlying medical conditions (such as diabetes), avoid unnecessary antibiotic use, and rinse your mouth after using corticosteroids. If you wear dentures, clean them regularly and ensure they fit properly.
3. **Q: Is oral thrush contagious?**
**A:** Oral thrush is not typically contagious in healthy individuals. However, it can be transmitted to infants during breastfeeding if the mother has a *Candida* infection on her nipples.
4. **Q: Can oral thrush cause any long-term complications?**
**A:** Untreated oral thrush can lead to complications such as difficulty eating and swallowing, dehydration, and the spread of the infection to other parts of the body. In severe cases, systemic candidiasis can be life-threatening.
5. **Q: Are there any natural remedies for oral thrush?**
**A:** Some natural remedies, such as yogurt with live cultures and coconut oil, may help to alleviate the symptoms of oral thrush. However, these remedies are not a substitute for medical treatment and should be used in consultation with a healthcare professional.
6. **Q: How long does it take for Nystatin to start working?**
**A:** Most patients experience noticeable improvement in their symptoms within 2-3 days of starting Nystatin treatment. However, it’s important to complete the full course of medication to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
7. **Q: What should I do if Nystatin doesn’t work?**
**A:** If Nystatin is not effective in treating your oral thrush, consult with your healthcare provider. They may recommend alternative antifungal medications, such as Clotrimazole or Fluconazole.
8. **Q: Can oral thrush affect my sense of taste?**
**A:** Yes, oral thrush can sometimes affect your sense of taste, making foods taste bland or metallic.
9. **Q: Are there any dietary changes that can help with oral thrush?**
**A:** Limiting your intake of sugary and processed foods can help to control the growth of *Candida* in the mouth. Consider adding probiotic-rich foods to your diet to promote a healthy balance of microorganisms.
10. **Q: How is oral thrush diagnosed?**
**A:** Oral thrush is typically diagnosed based on a visual examination of the mouth. In some cases, a sample of the infected tissue may be taken and sent to a laboratory for further analysis.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding oral thrush and the relevant ICD-10 codes is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and proper medical documentation. Nystatin oral suspension remains a valuable tool in managing this common condition, offering targeted antifungal action and a well-established safety profile. By addressing the underlying causes, managing risk factors, and adhering to recommended treatment guidelines, individuals can effectively combat oral thrush and restore their oral health. We’ve aimed to provide a resource reflecting our deep understanding of oral thrush and its management.
To further enhance your knowledge and understanding of oral health, we encourage you to explore our other comprehensive guides and resources. Share your experiences with oral thrush and Nystatin treatment in the comments below. If you have specific concerns or require personalized advice, contact our experts for a consultation on oral thrush management. Your oral health is our priority, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
