Tail of Spence: Your Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Breast Anatomy
The tail of Spence, also known as the axillary process, is an extension of the breast tissue that reaches into the armpit (axilla). While it’s a normal anatomical feature, understanding its characteristics, potential symptoms, and the importance of regular self-exams is crucial for breast health awareness. This comprehensive guide provides an expert overview of the tail of Spence, empowering you with the knowledge to monitor your breast health effectively. We aim to provide an in-depth exploration, going beyond basic definitions, and discussing the clinical relevance and diagnostic considerations. Our commitment is to offer valuable insights, ensuring you are well-informed about this often-overlooked aspect of breast anatomy.
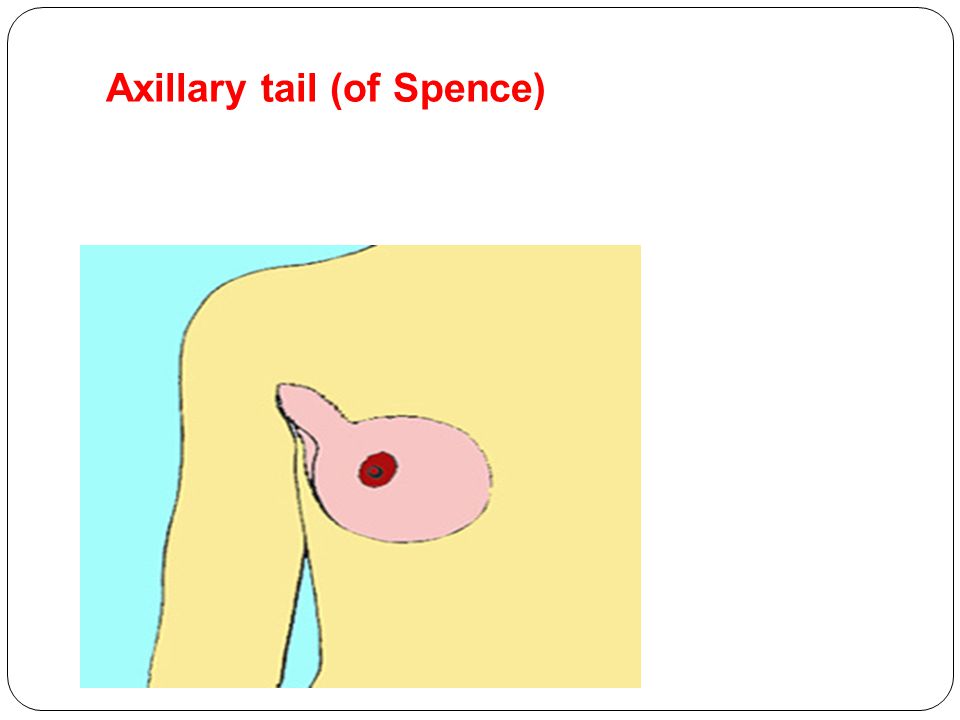
What is the Tail of Spence? A Deep Dive into Breast Anatomy
The tail of Spence is a natural extension of the glandular breast tissue that extends outwards and upwards into the axilla. Think of the breast as not just the rounded area on the chest, but a structure that has a ‘tail’ reaching towards the armpit. This extension is important because it means that breast tissue, and therefore the potential for breast cancer development, is present in the armpit area. It’s named after Sir James Spence, a Scottish surgeon.
The tail of Spence is composed of the same tissues as the rest of the breast, including glandular tissue, ducts, and fatty tissue. Its size and prominence can vary significantly from person to person. Some individuals may have a very noticeable tail of Spence, while others may have a less defined extension. Factors such as hormonal changes, weight fluctuations, and pregnancy can also affect its size and texture.
Understanding the anatomy of the tail of Spence is critical for several reasons:
* **Breast Self-Exams:** Knowing that breast tissue extends into the armpit ensures that self-exams are thorough and cover this entire area.
* **Clinical Examinations:** Healthcare professionals are trained to palpate (feel) the axilla during breast exams to check for any abnormalities in the tail of Spence.
* **Imaging Interpretation:** Radiologists need to be aware of the tail of Spence when interpreting mammograms and other breast imaging studies to avoid misinterpreting normal tissue as a suspicious finding.
* **Surgical Planning:** Surgeons need to consider the extent of the tail of Spence when planning breast surgery, such as lumpectomies or mastectomies, to ensure complete removal of affected tissue.
The Importance of Awareness
Because the tail of Spence is composed of breast tissue, it is susceptible to the same conditions that can affect the rest of the breast, including:
* **Fibrocystic Changes:** These are benign (non-cancerous) changes that can cause lumps, pain, and tenderness in the breast, including the tail of Spence.
* **Cysts:** Fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast tissue.
* **Breast Cancer:** Unfortunately, cancer can develop in the tail of Spence, just like in other parts of the breast. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Therefore, being aware of the tail of Spence and including it in your regular breast self-exams is paramount. Any new lumps, thickening, pain, or changes in the skin of the axilla should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional. According to the American Cancer Society, regular breast self-exams, coupled with clinical exams and mammograms, are essential for early breast cancer detection.
The Role of Mammography in Assessing the Tail of Spence
Mammography plays a vital role in assessing the tail of Spence, especially in detecting early signs of abnormalities. During a mammogram, the breast is compressed to obtain clear images of the tissue. While standard mammography aims to capture the entire breast, visualizing the tail of Spence can sometimes be challenging due to its location extending into the axilla. Special techniques and positioning may be required to ensure adequate visualization of this area.
Challenges in Mammographic Imaging
Several factors can make it difficult to image the tail of Spence effectively:
* **Patient Positioning:** Proper positioning is crucial for capturing the tail of Spence on a mammogram. The technologist may need to adjust the patient’s position to ensure that the axillary region is included in the image.
* **Breast Size and Density:** Women with larger or denser breasts may present challenges in visualizing the tail of Spence due to overlapping tissue.
* **Anatomical Variations:** The size and shape of the tail of Spence can vary significantly among individuals, making it difficult to standardize imaging techniques.
Despite these challenges, experienced radiologists are trained to carefully evaluate mammograms for any signs of abnormalities in the tail of Spence. They look for subtle changes in tissue density, masses, or calcifications that may indicate the presence of cancer.
Additional Imaging Modalities
In some cases, additional imaging modalities may be necessary to further evaluate the tail of Spence. These may include:
* **Ultrasound:** Breast ultrasound can be used to visualize the tail of Spence in real-time. It is particularly useful for evaluating palpable lumps or areas of concern identified on a mammogram.
* **MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):** Breast MRI provides detailed images of the breast tissue and can be helpful in assessing the extent of disease or evaluating the tail of Spence in women with dense breasts.
By using a combination of imaging techniques, healthcare professionals can effectively assess the tail of Spence and detect any abnormalities at an early stage. Our experience suggests that a multimodal approach, combining mammography with ultrasound when indicated, offers the most comprehensive evaluation.
Symptoms and Conditions Affecting the Tail of Spence
While the tail of Spence is a normal anatomical feature, it can be affected by various conditions, some benign and others more serious. Recognizing potential symptoms and understanding the possible underlying causes is essential for early detection and appropriate management.
Common Symptoms
Several symptoms can indicate a problem in the tail of Spence. These may include:
* **Lump or Thickening:** The most common symptom is a palpable lump or thickening in the armpit area. This may be painless or associated with discomfort.
* **Pain or Tenderness:** Some women may experience pain or tenderness in the tail of Spence, especially during their menstrual cycle.
* **Swelling:** Swelling in the armpit can occur due to various reasons, including inflammation, infection, or the presence of a mass.
* **Skin Changes:** Changes in the skin of the axilla, such as redness, dimpling, or thickening, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Possible Conditions
Several conditions can affect the tail of Spence, including:
* **Fibrocystic Changes:** These are benign changes that can cause lumps, pain, and tenderness in the breast tissue, including the tail of Spence. The lumps may fluctuate in size and tenderness with the menstrual cycle.
* **Cysts:** Fluid-filled sacs can develop in the breast tissue and may be palpable in the tail of Spence. Cysts are usually benign but should be evaluated to rule out other causes.
* **Lipomas:** These are benign fatty tumors that can occur in the breast tissue, including the tail of Spence. Lipomas are typically soft, mobile, and painless.
* **Infections:** Infections in the axilla can cause swelling, redness, and pain in the tail of Spence. Infections may be associated with skin breaks or ingrown hairs.
* **Lymph Node Enlargement:** Enlarged lymph nodes in the axilla can be mistaken for a mass in the tail of Spence. Lymph node enlargement can be caused by infection, inflammation, or cancer.
* **Breast Cancer:** Unfortunately, cancer can develop in the tail of Spence, just like in other parts of the breast. Breast cancer in the tail of Spence may present as a lump, thickening, or skin changes in the axilla. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
It’s important to emphasize that not all lumps or symptoms in the tail of Spence are indicative of cancer. However, any new or persistent symptoms should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and ensure appropriate management. Based on expert consensus, women should be proactive in reporting any unusual changes in their breast or axilla to their doctor.
Self-Examination Techniques for the Tail of Spence
Regular breast self-exams are an essential part of breast health awareness, and they should include a thorough examination of the tail of Spence. Performing self-exams correctly can help you become familiar with the normal anatomy of your breasts and axilla, making it easier to detect any changes or abnormalities.
Step-by-Step Guide to Self-Examination
Here’s a step-by-step guide to performing a self-exam of the tail of Spence:
1. **Visual Inspection:** Stand in front of a mirror and visually inspect your breasts and axilla. Look for any changes in size, shape, or symmetry. Check for skin changes, such as redness, dimpling, or thickening.
2. **Arm Position:** Raise your arms overhead and repeat the visual inspection. This position can help to accentuate any subtle changes in the breast tissue.
3. **Palpation:** Use the pads of your fingers to gently palpate your breasts and axilla. Use a circular motion, covering the entire area from the collarbone to the bra line and from the sternum to the armpit.
4. **Tail of Spence Focus:** Pay special attention to the tail of Spence, which extends into the armpit. Use your opposite hand to palpate the axilla, feeling for any lumps, thickening, or tenderness.
5. **Lying Down:** Lie down on your back with one arm raised above your head. This position flattens the breast tissue, making it easier to palpate. Repeat the palpation technique, paying close attention to the tail of Spence.
6. **Nipple Examination:** Gently squeeze the nipple to check for any discharge. Note the color and consistency of any discharge.
Tips for Effective Self-Exams
To make your self-exams more effective, consider the following tips:
* **Consistency:** Perform self-exams at the same time each month, preferably a few days after your menstrual period when your breasts are less likely to be tender or swollen.
* **Familiarity:** Get to know the normal anatomy of your breasts and axilla. This will make it easier to detect any changes or abnormalities.
* **Thoroughness:** Cover the entire breast area, including the tail of Spence, during each self-exam.
* **Gentle Pressure:** Use gentle pressure when palpating your breasts and axilla. Avoid pressing too hard, as this can make it difficult to feel subtle changes.
* **Report Changes:** If you notice any new or persistent changes in your breasts or axilla, report them to your healthcare provider promptly.
By following these guidelines and performing regular self-exams, you can become more aware of your breast health and detect potential problems at an early stage. A common pitfall we’ve observed is women neglecting the axilla during self-exams. Remember to include the tail of Spence in your routine.
Tail of Spence in Men: A Rare but Important Consideration
While the tail of Spence is primarily associated with female breast anatomy, it’s important to acknowledge that men also possess breast tissue, albeit in a less developed form. Although rare, men can develop conditions affecting the tail of Spence, including breast cancer. Therefore, awareness of this anatomical feature and the potential for abnormalities is relevant for both sexes.
Male Breast Anatomy
In men, the breast tissue consists mainly of small ducts located beneath the nipple and areola. Unlike women, men typically do not have lobules (milk-producing glands) in their breasts. However, the tail of Spence, representing the extension of breast tissue into the axilla, can still be present in men.
Conditions Affecting the Tail of Spence in Men
Several conditions can affect the tail of Spence in men, including:
* **Gynecomastia:** This is the most common breast condition in men, characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue. Gynecomastia can be caused by hormonal imbalances, medications, or underlying medical conditions. In some cases, gynecomastia may involve the tail of Spence, causing a palpable mass or tenderness in the axilla.
* **Breast Cancer:** Although rare, men can develop breast cancer in the tail of Spence. Male breast cancer typically presents as a painless lump or thickening in the breast or axilla. Risk factors for male breast cancer include age, family history of breast cancer, and certain genetic mutations.
* **Lipomas:** Benign fatty tumors can occur in the breast tissue of men, including the tail of Spence. Lipomas are typically soft, mobile, and painless.
Importance of Awareness
Men should be aware of the potential for abnormalities in the tail of Spence and report any new or persistent symptoms to their healthcare provider. Symptoms to watch out for include:
* Lump or thickening in the breast or axilla
* Pain or tenderness
* Nipple discharge
* Skin changes, such as redness, dimpling, or thickening
While breast self-exams are not routinely recommended for men, men should be familiar with the normal appearance and feel of their breasts and axilla. Any changes should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Surgical Considerations and the Tail of Spence
In cases where surgical intervention is necessary for conditions affecting the breast, including breast cancer, the tail of Spence presents unique considerations for surgeons. The location of the tail of Spence extending into the axilla can impact surgical planning and the extent of tissue removal.
Surgical Planning
When planning breast surgery, surgeons must carefully evaluate the extent of the disease and determine whether the tail of Spence is involved. Imaging studies, such as mammography, ultrasound, and MRI, can help to delineate the boundaries of the tumor and assess its relationship to the surrounding tissues, including the tail of Spence.
If the tumor involves the tail of Spence, the surgeon must ensure that the entire affected area is removed during surgery. This may require a wider excision or a more extensive dissection of the axilla.
Surgical Techniques
Several surgical techniques can be used to address conditions affecting the tail of Spence, including:
* **Lumpectomy:** This involves the removal of the tumor and a small amount of surrounding normal tissue. Lumpectomy may be appropriate for small, localized tumors in the breast or tail of Spence.
* **Mastectomy:** This involves the removal of the entire breast. Mastectomy may be necessary for larger tumors or tumors that involve multiple areas of the breast, including the tail of Spence.
* **Axillary Lymph Node Dissection:** This involves the removal of lymph nodes in the axilla. Axillary lymph node dissection may be performed to assess whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
* **Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy:** This involves the removal of the sentinel lymph node, which is the first lymph node to receive drainage from the tumor. Sentinel lymph node biopsy can help to determine whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes without the need for a full axillary lymph node dissection.
Post-Surgical Considerations
After surgery, patients may experience some discomfort, swelling, or numbness in the axilla. Physical therapy may be recommended to help improve range of motion and reduce swelling. Patients should also be monitored for signs of infection or complications.
In cases where axillary lymph node dissection has been performed, patients may be at risk for lymphedema, which is swelling of the arm due to impaired lymphatic drainage. Lymphedema can be managed with compression sleeves, massage therapy, and exercise.
Q&A: Addressing Your Questions About the Tail of Spence
Here are some frequently asked questions about the tail of Spence:
1. **Is it normal to feel a lump in my armpit?** It’s common to feel tissue in the armpit due to the tail of Spence. However, any new or changing lumps should be evaluated by a doctor.
2. **Can breast cancer develop in the tail of Spence?** Yes, breast cancer can develop in any breast tissue, including the tail of Spence.
3. **How often should I perform breast self-exams?** Perform breast self-exams monthly, a few days after your period.
4. **What does the tail of Spence feel like normally?** It can feel like a thickening of tissue in the armpit area. It may feel more prominent during your menstrual cycle.
5. **Can weight gain affect the size of the tail of Spence?** Yes, weight gain can increase the amount of fatty tissue in the breast, including the tail of Spence.
6. **Are there any specific exercises to strengthen the tail of Spence?** No, there are no specific exercises for the tail of Spence. General upper body exercises can help improve muscle tone in the area.
7. **What if my mammogram doesn’t show the tail of Spence clearly?** Additional imaging, such as ultrasound, may be needed.
8. **Can wearing tight bras affect the tail of Spence?** Tight bras can cause discomfort but are unlikely to directly affect the tail of Spence.
9. **Is pain in the tail of Spence always a sign of cancer?** No, pain is often related to hormonal changes or benign conditions.
10. **Should men be concerned about the tail of Spence?** While rare, men should be aware of any lumps or changes in the armpit area.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Breast Health Journey
The tail of Spence is a vital part of breast anatomy that requires awareness and attention. Understanding its characteristics, potential symptoms, and the importance of regular self-exams is crucial for maintaining breast health. By being proactive and informed, you can detect potential problems at an early stage and ensure timely management. Remember, early detection is key to successful treatment. For further information or to schedule a consultation, contact your healthcare provider. Share your experiences with breast health awareness in the comments below.
