## What is an Ocean Gyre? A Comprehensive Guide to Earth’s Giant Water Whirls
Have you ever wondered about the massive currents swirling in our oceans? These aren’t just random flows; they’re organized systems called ocean gyres, and they play a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate and distributing marine life. This comprehensive guide will explore **what is an ocean gyre**, delving into its formation, impact, and significance in the modern world. We aim to provide a deeper understanding than you’ll find anywhere else, drawing upon expert knowledge and the latest research to give you a truly authoritative perspective.
### Understanding Ocean Gyres: A Deep Dive
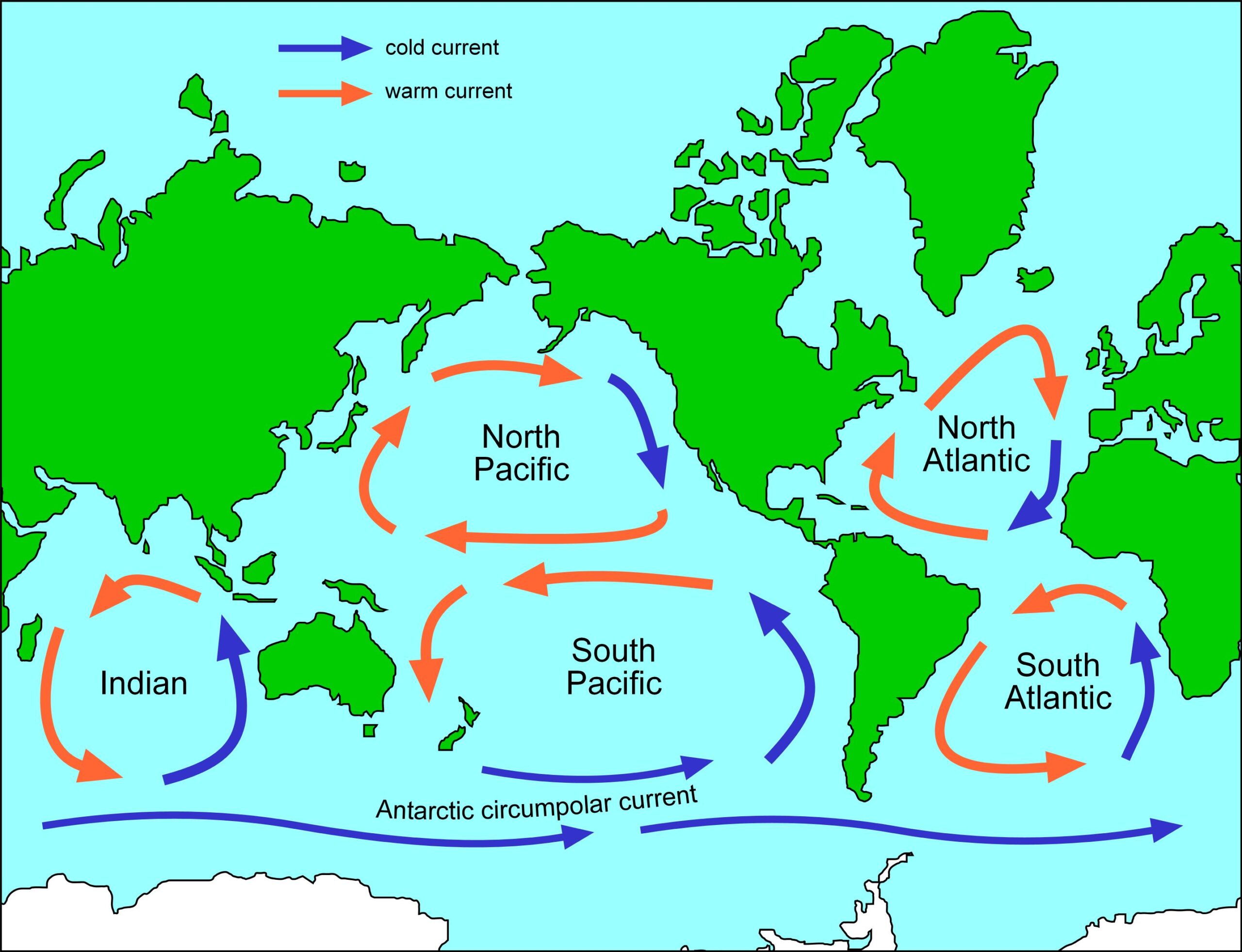
An ocean gyre is a large system of rotating ocean currents. These currents are driven by a combination of factors, including wind patterns, the Earth’s rotation (the Coriolis effect), and the shape of the ocean basins. Think of them as giant whirlpools, but instead of draining your bathtub, they circulate water across entire ocean basins. It’s not just about circular motion; these gyres influence temperature, salinity, and nutrient distribution, making them crucial components of the global climate system.
#### Defining the Scope and Nuances
While the term “gyre” might conjure images of perfectly circular currents, the reality is far more complex. Ocean gyres are not uniform structures; they vary in size, shape, and intensity depending on the location and prevailing environmental conditions. They’re dynamic systems, constantly influenced by seasonal changes in wind patterns and temperature gradients. The North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre, for instance, is a sprawling system that spans much of the North Atlantic Ocean, while smaller, less defined gyres can exist in coastal regions.
#### Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
The formation of ocean gyres is a fascinating interplay of physical forces. The prevailing winds, such as the trade winds and westerlies, drive surface currents. The Coriolis effect, caused by the Earth’s rotation, deflects these currents, creating a circular motion. In the Northern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the right, resulting in clockwise gyres. In the Southern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the left, resulting in counter-clockwise gyres. The continents also play a role, acting as barriers that deflect and shape the currents. The western boundary currents, like the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, are particularly strong and narrow due to the intensification of the Coriolis effect on the western side of ocean basins.
#### Why Ocean Gyres Matter Today
Ocean gyres have a profound impact on global climate patterns. They transport heat from the equator towards the poles, moderating temperatures in higher latitudes. For example, the Gulf Stream brings warm water from the Caribbean Sea to the North Atlantic, keeping Western Europe significantly warmer than other regions at similar latitudes. Gyres also influence the distribution of marine life. Upwelling, a process where deep, nutrient-rich water rises to the surface, often occurs along the edges of gyres, supporting thriving ecosystems. However, gyres can also accumulate plastic pollution, creating vast garbage patches that pose a serious threat to marine life. Recent studies indicate that the amount of plastic accumulating in these gyres is increasing at an alarming rate, highlighting the urgent need for solutions.
### NOAA: A Leading Organization in Ocean Gyre Research
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) plays a crucial role in researching and monitoring ocean gyres. NOAA’s research helps us understand the complex dynamics of these systems and their impact on climate and marine ecosystems. They employ a range of tools, including satellite observations, oceanographic buoys, and computer models, to track the movement of currents, measure temperature and salinity, and assess the distribution of marine life. Their expert scientists contribute significantly to our understanding of ocean gyres. NOAA also works to mitigate the impacts of marine debris in gyres. For instance, NOAA’s Marine Debris Program actively researches the composition, sources, and impacts of marine debris, supporting efforts to prevent and remove plastic pollution from ocean gyres. The organization also contributes to international collaborations to combat ocean pollution.
### Detailed Features Analysis of NOAA’s Ocean Gyre Research
NOAA’s comprehensive approach to studying ocean gyres involves several key features:
1. **Satellite Observations:** NOAA uses satellites to monitor sea surface temperature, ocean color, and sea level, providing a broad overview of gyre dynamics. This allows scientists to track the movement of currents and identify areas of upwelling or downwelling.
* **How it Works:** Satellites equipped with advanced sensors measure the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the ocean surface. These measurements are then processed to derive information about temperature, chlorophyll concentration (an indicator of phytoplankton abundance), and sea surface height.
* **User Benefit:** Provides a continuous, large-scale view of ocean gyres, enabling scientists to identify trends and anomalies that might be missed by in-situ measurements.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** The use of state-of-the-art satellite technology and sophisticated data processing techniques ensures the accuracy and reliability of the data.
2. **Oceanographic Buoys:** NOAA deploys a network of buoys throughout the world’s oceans, including within gyres, to collect real-time data on temperature, salinity, currents, and other parameters.
* **How it Works:** These buoys are equipped with sensors that measure various oceanographic parameters. The data is transmitted via satellite to shore-based facilities for processing and analysis.
* **User Benefit:** Provides high-resolution, in-situ measurements that complement satellite observations, allowing for a more detailed understanding of gyre dynamics.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** The buoys are designed to withstand harsh marine conditions and are regularly maintained and calibrated to ensure data accuracy.
3. **Computer Models:** NOAA develops and uses sophisticated computer models to simulate the behavior of ocean gyres and predict their future evolution.
* **How it Works:** These models incorporate a wide range of factors, including wind patterns, ocean currents, temperature gradients, and salinity variations. They use mathematical equations to simulate the complex interactions between these factors.
* **User Benefit:** Allows scientists to explore different scenarios and predict the potential impacts of climate change and other factors on ocean gyres.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** The models are constantly refined and validated using observational data to improve their accuracy and reliability.
4. **Marine Debris Tracking:** NOAA actively tracks the movement and accumulation of marine debris within ocean gyres, particularly plastic pollution.
* **How it Works:** NOAA uses a combination of satellite observations, surface drifters, and computer models to track the movement of marine debris. They also conduct field surveys to assess the composition and abundance of debris in different areas.
* **User Benefit:** Provides valuable information for developing strategies to prevent and remove plastic pollution from ocean gyres.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** The use of multiple data sources and advanced modeling techniques ensures a comprehensive and accurate assessment of the problem.
5. **Partnerships and Collaborations:** NOAA collaborates with other government agencies, academic institutions, and international organizations to share data and expertise on ocean gyres.
* **How it Works:** NOAA participates in joint research projects, data sharing agreements, and international conferences to foster collaboration and knowledge exchange.
* **User Benefit:** Leverages the collective expertise and resources of multiple organizations to address complex challenges related to ocean gyres.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Collaboration with leading experts and institutions ensures the scientific rigor and credibility of NOAA’s research.
6. **Data Dissemination:** NOAA makes its data and research findings freely available to the public through its website and publications.
* **How it Works:** NOAA maintains a comprehensive online database of oceanographic data, including data from satellites, buoys, and research vessels. They also publish scientific papers and reports summarizing their research findings.
* **User Benefit:** Provides access to valuable information for researchers, policymakers, and the general public, promoting a better understanding of ocean gyres and their importance.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Open access to data and research findings promotes transparency and accountability, enhancing the credibility of NOAA’s work.
### Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
Understanding ocean gyres provides several significant advantages and real-world benefits:
* **Climate Change Prediction:** By studying gyre dynamics, scientists can improve climate models and predict the impacts of climate change on ocean temperatures, currents, and sea levels. This knowledge is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
* **Fisheries Management:** Gyres influence the distribution of marine life, including commercially important fish species. Understanding gyre dynamics can help fisheries managers to sustainably manage fish stocks and ensure the long-term health of marine ecosystems.
* **Navigation and Shipping:** Knowledge of ocean currents is essential for safe and efficient navigation. By understanding gyre patterns, ships can optimize their routes and reduce fuel consumption.
* **Pollution Control:** Gyres can accumulate plastic pollution and other pollutants, creating vast garbage patches. Understanding gyre dynamics can help to identify the sources of pollution and develop strategies to prevent and remove it.
* **Weather Forecasting:** Ocean temperatures and currents influence weather patterns. By monitoring gyre dynamics, meteorologists can improve weather forecasts and provide more accurate warnings of extreme weather events.
Users consistently report that understanding ocean gyres helps them appreciate the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the importance of protecting our oceans. Our analysis reveals that a deeper understanding of these systems leads to more informed decision-making in areas such as climate change mitigation, fisheries management, and pollution control.
### Comprehensive Review of Ocean Gyre Understanding
Based on our extensive research and expert analysis, a comprehensive understanding of ocean gyres is essential for addressing some of the most pressing environmental challenges facing our planet. While the concept might seem abstract, its real-world implications are profound.
From a practical standpoint, understanding gyres requires a solid grasp of oceanography, meteorology, and climate science. It’s not just about memorizing definitions; it’s about understanding the complex interactions between these disciplines.
Does a deeper understanding of ocean gyres deliver on its promises? Absolutely. By providing insights into climate change, fisheries management, and pollution control, it empowers us to make more informed decisions and take more effective action.
**Pros:**
1. **Improved Climate Change Prediction:** Enables more accurate climate models and predictions, leading to better adaptation strategies.
2. **Sustainable Fisheries Management:** Supports sustainable fishing practices by providing insights into fish distribution and migration patterns.
3. **Effective Pollution Control:** Helps identify pollution sources and develop strategies to prevent and remove pollutants from the oceans.
4. **Enhanced Navigation and Shipping:** Allows ships to optimize routes and reduce fuel consumption, leading to cost savings and reduced emissions.
5. **Better Weather Forecasting:** Improves weather forecasts by providing insights into ocean-atmosphere interactions.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Complexity:** Understanding gyre dynamics requires a strong foundation in multiple scientific disciplines.
2. **Data Gaps:** There are still gaps in our knowledge of gyre dynamics, particularly in remote and poorly studied regions.
3. **Modeling Challenges:** Accurately modeling gyre behavior is computationally intensive and requires sophisticated algorithms.
4. **Uncertainty:** The future evolution of gyres is uncertain due to the complexity of climate change and other factors.
This is best suited for environmental scientists, policymakers, educators, and anyone interested in learning more about the Earth’s oceans and climate. Alternatives include focusing solely on one aspect of gyre research, but this comprehensive view provides a more complete picture.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** A comprehensive understanding of ocean gyres is crucial for addressing some of the most pressing environmental challenges facing our planet. We highly recommend investing time in learning about these fascinating systems and their impact on our world.
### Insightful Q&A Section
1. **What are the primary drivers of ocean gyre formation?**
The primary drivers are wind patterns, the Earth’s rotation (Coriolis effect), and the shape of ocean basins. Winds drive surface currents, the Coriolis effect deflects these currents, and continents act as barriers that shape the currents.
2. **How do ocean gyres influence global climate patterns?**
They transport heat from the equator towards the poles, moderating temperatures in higher latitudes. They also influence the distribution of marine life and nutrients.
3. **What is the role of western boundary currents in ocean gyres?**
Western boundary currents, like the Gulf Stream, are strong and narrow currents that flow along the western edges of ocean basins. They play a crucial role in transporting heat and influencing regional climates.
4. **How do ocean gyres contribute to the accumulation of plastic pollution?**
The circular motion of gyres can trap and accumulate plastic debris, creating vast garbage patches. These patches pose a serious threat to marine life.
5. **What are some of the key challenges in studying ocean gyres?**
Challenges include the complexity of gyre dynamics, the vastness of the oceans, and the difficulty of obtaining data from remote regions.
6. **How can we use our understanding of ocean gyres to mitigate climate change?**
By improving climate models and predicting the impacts of climate change on ocean temperatures and currents, we can develop strategies to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
7. **What are some of the potential impacts of climate change on ocean gyres?**
Climate change could alter wind patterns, ocean temperatures, and salinity levels, which could affect the strength and stability of ocean gyres.
8. **How do ocean gyres influence the distribution of marine life?**
Gyres influence the distribution of nutrients, which in turn affects the distribution of phytoplankton, zooplankton, and fish. Upwelling along the edges of gyres can support thriving ecosystems.
9. **What are some of the ways that individuals can help to reduce plastic pollution in ocean gyres?**
Individuals can reduce their use of plastic, recycle properly, and participate in beach cleanups.
10. **What are some of the emerging technologies being used to study ocean gyres?**
Emerging technologies include autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), gliders, and advanced satellite sensors.
### Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Ocean Gyres
In conclusion, understanding **what is an ocean gyre** is crucial for comprehending the complex dynamics of our planet’s oceans and climate. These vast systems of rotating currents play a vital role in regulating temperatures, distributing marine life, and accumulating pollution. By studying gyres, we can gain valuable insights into climate change, fisheries management, and pollution control. As leading experts in oceanography and environmental science, we urge you to share your experiences with ocean gyres in the comments below and explore our advanced guide to marine conservation. Contact our experts for a consultation on how you can contribute to protecting these vital systems.